Executing Java Program : Introduction
- This section is all about knowing internal working of Java program , i.e. how a Java code is converted to byte-code , how it compiles and what are the resources required in executing Java program.
- Prior to executing java program, it passes through two phase i.e. compile time and runtime. We will discuss about both these phases.
Executing Java Program : Compile Time
- At compile time the Java source code (Program.java) is compiled using javac compiler and is converted into Java Byte codes known as .class file.
- Javac is the primary Java compiler which is included in Java Development Kit. It converts .java into .class file.
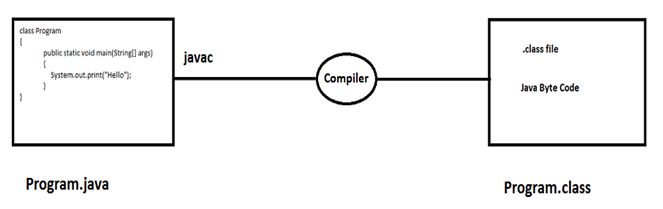
Step-1 : Compile Time
Executing Java Program : Run Time
- Once the Java code is compiled through compiler and gets converted into Byte codes thereafter the responsibility is handled by JVM.
- Class loader loads the class in main memory (heap area) and the byte-code verifier does the detailed checking of the segment of code for any fragment of code like illegal pointers etc. that can violate access right. It ensures the code passed to the Java interpreter is in fit state to be executed and can run smoothly.
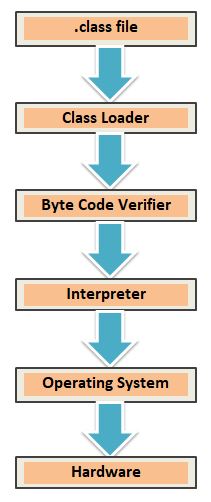
Step-2 : Run Time
- Java Interpreter then reads and executes byte stream that is converted by JVM from byte-codes to machine language.
- Then it further passes to runtime system of JVM and finally links to hardware via JVM.